Cold Storage Warehouse 3PLs: Specialized Solutions for Temperature-Sensitive Supply Chains

Last updated on February 28, 2025

In this article
 16 minutes
16 minutes
- Understanding Cold Storage 3PLs
- Definition and Purpose of Cold Storage Warehousing
- Advantages of Cold Storage Solutions
- Comprehensive Cold Chain Services
- Comprehensive International Cold Chain Integrity Shipping
- Addressing Cold Storage Challenges
- Choosing the Right Cold Storage 3PL Partner
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
In today’s global supply chain landscape, specialized third-party logistics (3PL) providers offering cold storage capabilities have become essential partners for businesses dealing with temperature-sensitive products. The cold storage market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 9.2% from 2022 to 2030, highlighting its growing significance and popularity. From pharmaceuticals and biologics to fresh produce and frozen foods, these specialized 3PLs ensure product integrity throughout the storage and distribution process.
Understanding Cold Storage 3PLs
Cold storage 3PLs provide specialized warehouse and logistics services designed specifically for temperature-controlled products. Unlike traditional warehousing, cold storage facilities maintain precise temperature ranges to preserve product quality, extend shelf life, and comply with regulatory requirements. Cold storage construction involves creating specialized storage solutions required for temperature-sensitive products, highlighting its significance in the supply chain with unique design considerations and costs that differentiate it from conventional structures.
Definition and Purpose of Cold Storage Warehousing
Cold storage warehousing refers to the specialized storage of perishable goods at controlled temperatures to maintain their quality and extend their shelf life. This type of warehousing is crucial for products that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and certain chemicals. The primary purpose of cold storage warehousing is to provide a consistent and reliable environment that prevents spoilage and damage, ensuring that temperature-sensitive products remain safe and effective throughout their storage period. By maintaining specific temperature conditions, cold storage facilities help businesses comply with regulatory requirements and meet the high standards expected by consumers and industry stakeholders.
Advantages of Cold Storage Solutions
Cold storage solutions offer numerous advantages that are vital for the efficient management of temperature-sensitive supply chains. One of the most significant benefits is the extended shelf life of perishable goods, which reduces the risk of spoilage and waste. This not only improves product quality and safety but also leads to cost savings by minimizing losses. Additionally, cold storage solutions enhance supply chain efficiency by ensuring that products are stored under optimal conditions, which facilitates better inventory management and reduces the likelihood of stockouts or overstocking. Compliance with regulatory requirements is another critical advantage, as cold storage facilities are designed to meet stringent standards for temperature-sensitive products, ensuring that businesses remain compliant and avoid potential penalties.
Comprehensive Cold Chain Services
Modern cold storage 3PLs have evolved well beyond basic refrigerated warehousing to offer sophisticated end-to-end solutions that address every aspect of temperature-sensitive supply chains. They provide extensive cold storage services, leveraging a vast network and advanced capabilities to ensure temperature-controlled warehousing globally. These integrated services ensure product integrity throughout the entire logistics process.
Types of Cold Storage Facilities
Cold storage facilities come in various types, each designed to meet specific temperature requirements for different products:
- Refrigerated Cold Storage Facilities: These facilities maintain temperatures between 32°F and 50°F (0°C and 10°C) and are ideal for storing products that require refrigeration, such as meat, dairy, and fresh produce. The controlled environment helps preserve the freshness and quality of these items.
- Frozen Cold Storage Facilities: Maintaining temperatures below 0°F (-18°C), these facilities are used for storing products that need to be kept frozen, such as frozen foods and certain pharmaceuticals. The ultra-cold environment prevents microbial growth and preserves the integrity of the products.
- Ultra-Low Temperature Cold Storage Facilities: These facilities maintain temperatures below -20°F (-29°C) and are essential for storing products that require extremely low temperatures, such as specific pharmaceuticals and biological samples. The precise temperature control in these facilities ensures the stability and efficacy of highly sensitive products.
Temperature-Controlled Warehousing with Multiple Climate Zones
Today’s advanced cold storage facilities feature precisely engineered environments tailored to specific product requirements:
- Zone Segregation Technology: Modern facilities utilize high efficiency insulated walls, specialized air locks, and positive/negative pressure controls to maintain distinct temperature boundaries between adjacent storage areas while minimizing energy loss during transitions.
- Redundant Cooling Systems: Critical storage zones feature N+1 or N+2 redundancy in refrigeration equipment, with automatic failover capabilities and backup power generation that activates within seconds of utility power loss.
- Microclimate Mapping: Advanced facilities conduct comprehensive thermal mapping studies that identify temperature variations throughout storage spaces, allowing for strategic product placement based on sensitivity. These maps are updated seasonally to account for changing external conditions.
- Customizable Environments: Beyond standard frozen, refrigerated, and ambient zones, leading 3PLs now offer customizable environments with precise control over temperature, humidity, air exchange rates, and even light exposure for especially sensitive products like certain pharmaceuticals, biotechnology materials, and specialty foods. Cold air is essential in these environments to maintain product integrity, and evaporators play a crucial role in circulating this cold air, effectively chilling the environment and the goods within.
- High-Density Storage Solutions: Mobile racking systems designed specifically for cold environments maximize storage capacity while maintaining proper air circulation, reducing the refrigerated footprint and associated energy costs.
Specialized Transportation with Refrigerated Vehicles
Cold chain logistics presents unique challenges that require specialized equipment and expertise. Quality cold chain transportation has advanced significantly to maintain unbroken temperature control:
- Refrigerated Transport Fleets: Modern cold chain 3PLs operate specialized vehicle fleets including multi-temperature trailers capable of maintaining different zones within a single trailer (e.g., frozen, chilled, and ambient sections simultaneously). These vehicles incorporate redundant cooling systems, GPS tracking, and remote temperature monitoring. Many fleets now include hybrid or electric options for last-mile delivery in urban environments.
- Advanced Insulation Technology: Next-generation transport units utilize vacuum-insulated panels and phase-change materials that maintain stable temperatures longer, even during power outages or equipment failure.
- Continuous Temperature Monitoring: Advanced systems now employ multiple sensor points throughout cargo areas, transmitting data at 2-15 minute intervals via cellular or satellite connections. These systems integrate with blockchain platforms to create immutable temperature history records, and AI algorithms analyze patterns to predict and prevent potential excursions before they occur.
- Temperature Validation Procedures: Before loading begins, vehicles undergo pre-cooling to reach the target temperature. Products are equipped with calibrated temperature sensors during loading, and thermal imaging technology verifies proper temperature at critical handoff points. Loading docks feature air curtains and insulated dock seals to prevent temperature excursions during the transfer process.
- Immutable Temperature History Records: AI algorithms analyze patterns to predict and prevent potential excursions before they occur.
- Route Optimization for Temperature Integrity: Specialized routing algorithms account for ambient temperature forecasts, traffic patterns, and delivery time windows to minimize the risk of temperature excursions while optimizing fuel efficiency.
- Last-Mile Solutions: For final delivery, providers now offer options ranging from temperature-controlled vans with compartmentalized storage to specialized thermal packaging designed to maintain temperature for specific delivery window durations.
- Cross-Docking Infrastructure: Purpose-built temperature-controlled cross-docking facilities enable efficient transfer between long-haul and local delivery while maintaining the cold chain, featuring air curtains, rapid-roll doors, and thermal seals for loading docks.
The seamless integration between warehousing and transportation is critical. Modern systems allow for real-time visibility, enabling stakeholders to track both location and temperature conditions throughout the journey. This transparency has become increasingly important as regulatory requirements grow more stringent and consumers demand greater accountability.
Comprehensive International Cold Chain Integrity Shipping
The global movement of temperature-sensitive products presents unique challenges that modern cold storage 3PLs have developed sophisticated solutions to address. International cold chain logistics requires seamless temperature control across multiple transportation modes, handling points, and regulatory environments.
Specialized container technologies include active temperature-controlled containers with autonomous cooling, passive thermal packaging using vacuum-insulated panels and phase-change materials, and hybrid solutions that combine passive insulation with selective active cooling. Multi-modal transport coordination ensures seamless transfers between modes, temperature-mapped trade lanes for seasonal adjustments, and pre-conditioning protocols to stabilize shipments before transit.
Cold storage items require rigorous proof of proper handling and compliance with safety standards. Hence quality assurance and documentation is almost as important as the product itself. Quality assurance needs rigorous temperature mapping validation and clear chain-of-responsibility documentation at each handling point. Compliance with pre-clearance programs, temperature-controlled customs inspections, and global standards such as GDP, IATA, and industry best practices ensures regulatory alignment.
Advanced inventory management uses real-time shelf-life tracking, batch segregation, and temperature-based storage assignments to optimize efficiency and minimize waste. GPS monitoring provides real-time tracking, predictive risk management, and emergency intervention networks to prevent temperature excursions.
These are all unique storage and shipping complications for cold storage items not normally relevant for normal good storage.
Addressing Cold Storage Challenges
Cold storage warehousing presents several challenges that must be addressed to ensure the integrity and safety of temperature-sensitive products. Maintaining consistent temperatures, managing humidity levels, and ensuring proper inventory management are critical aspects of cold storage operations. Additionally, energy efficiency and regulatory compliance are significant concerns that impact both operational costs and the ability to meet industry standards. By understanding and addressing these challenges, businesses can optimize their cold storage processes and maintain the quality of their products.
Common Issues and Concerns in Cold Storage
Cold storage facilities face several common issues and concerns that can impact the quality and safety of temperature-sensitive products. Temperature fluctuations can cause damage to products, compromising their quality and safety. Proper humidity levels are crucial in cold storage to prevent moisture accumulation and condensation, which can lead to product damage and spoilage. Cold storage facilities require significant energy to maintain consistent temperatures, which can increase operating costs and environmental impact.
Efficient inventory management is critical in cold storage to ensure that products are stored and retrieved promptly, preventing overstocking, understocking, and spoilage. Cold storage facilities must comply with various regulatory requirements for temperature-sensitive products, including food safety and pharmaceutical storage standards. Adhering to these regulations is essential to avoid penalties and ensure product safety.
Value-Added Services for Temperature-Sensitive Products
Cold storage 3PLs now offer specialized shipping and handling services that extend well beyond basic storage; temperature-controlled processing areas for product manipulation maintained at appropriate temperatures, eliminating the need to move products to ambient conditions, cold packaging custom packaging services using materials validated for specific temperature ranges, including insulated containers, phase-change materials, and temperature-indicating devices, and cold-rated labeling materials and adhesives designed to maintain integrity in freezer environments, with condensation-resistant properties for items transitioning between temperature zones.
Compliance Management for Regulated Industries
There are many complex regulatory requirements for temperature-sensitive products; confirm your 3PL has the needed industry-specific certifications, such as HACCP, SQF, BRC, GDP (Good Distribution Practice), and specific pharmaceutical requirements from FDA, EMA, and other global regulatory bodies.
Beyond certifications, cold storage 3PLs need validation of monitoring systems according to industry standards, with documented calibration procedures and traceability to national standards and 21 CFR Part 11 compliant systems for industries requiring secure, tamper-evident electronic records with appropriate audit trails and electronic signature capabilities.
Automated generation of compliance documentation in industry-standard formats for submission to regulatory agencies, streamlining reporting processes while ensuring complete data inclusion is highly recommended.
Choosing the Right Cold Storage 3PL Partner
Selecting the optimal cold storage logistics partner represents a critical strategic decision that directly impacts product quality, regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Being part of professional associations like the American Frozen Food Institute (AFFI) and adhering to industry regulations is essential for ensuring a facility’s trustworthiness and compliance with food safety standards. Here’s a comprehensive framework for evaluating potential cold chain 3PL partners:
1. Temperature Range Capabilities and Stability
Beyond basic temperature classifications, businesses should conduct detailed evaluations of 3PL’s Temperature Mapping Documentation. Request comprehensive temperature mapping studies of potential facilities, including seasonal variations, recovery times after door openings, and identification of any hot/cold spots within storage areas to ensure the 3PL meets your cold storage requirements.
Evaluate historical temperature excursion data over multiple years, including duration, magnitude, and resolution response times. Leading providers maintain excursion rates below 0.1% of total monitored hours. Assess the provider’s approach to regular stability testing, including frequency of recalibration for monitoring systems and validation procedures for new storage areas or equipment.
Determine whether the provider can accommodate specialized temperature requirements outside standard ranges, such as ultra-low temperature storage (-80°C) for certain biologics or precise temperature control for pharmaceutical stability testing if needed.
Examine data on temperature recovery times following routine operations like loading/unloading or maintenance activities, which indicates the robustness of cooling systems.
2. Regulatory Compliance History and Certifications
A provider’s compliance history offers critical insights into their operational discipline. Verify relevant certifications appropriate to your industry, which might include BRC Global Standard for Storage and Distribution, ISO 9001, HACCP certification, FDA registration, or pharmaceutical-specific certifications like GDP (Good Distribution Practice).
Request summaries of recent regulatory inspections and third-party audits, including any observations or findings and, crucially, the corrective actions implemented in response. Evaluate the structure and effectiveness of the provider’s internal compliance department, including staffing ratios, qualification requirements, and authority within the organization. Assess the maturity of quality management systems, including change control procedures, deviation management, and documentation practices that would support your compliance requirements.
Finally, review the frequency and depth of regulatory training provided to staff, including how training effectiveness is measured and verified.
3. Technology Infrastructure and Monitoring Systems
Modern cold chain logistics requires sophisticated technological capabilities. Evaluate the design of temperature monitoring systems, including sensor redundancy, backup power supplies, and alert escalation protocols. Leading providers employ multiple independent monitoring systems as a safeguard against single-point failures.
Assess how monitoring data is made available to clients, including real-time dashboard capabilities, API integration options with client systems, and historical data retrieval functionality. Review security protocols protecting monitoring systems and client data, including penetration testing history, access controls, and security incident response procedures.
For regulated industries, verify the existence of computer system validation according to GAMP 5 or similar standards, ensuring that monitoring systems are demonstrably reliable for regulatory purposes.
4. Geographic Coverage and Transportation Network
Logistics network capabilities significantly impact service levels and risk profiles. Unlike standard products, 3PL locations need to be evaluated against your manufacturing sites, key suppliers, and customer destinations to minimize transit times and handoff points. Confirm whether the provider operates their own temperature-controlled transportation fleet or relies on partners; directly controlled assets often provide more consistent temperature management.
Review performance data for final delivery operations, including on-time delivery rates, temperature compliance during the critical last mile, and customer satisfaction scores. Evaluate the provider’s ability to reroute shipments or relocate inventory in response to facility issues, weather events, or other disruptions that might impact a single location.
5. Industry-Specific Experience and Expertise
Specialized knowledge significantly enhances operational performance. Identify the percentage of the provider’s business dedicated to your specific industry, as this often correlates with their depth of relevant expertise and processes tailored to your needs.
Assess whether the provider has established handling procedures specific to your product types, such as specialized procedures for vaccines, cell therapies, or delicate food products. Review the provider’s involvement in industry-specific organizations and standards committees, which often indicates commitment to best practices and awareness of emerging trends.
Request detailed case studies and client references specific to your industry, including examples of how they’ve solved challenges similar to those you might face.
6. Contingency Planning and Backup Systems
Robust backup systems and emergency preparedness are essential for cold chain integrity. Evaluate backup power generation capacity, including regular testing protocols, fuel supply agreements, and automatic transfer switch testing. Leading providers maintain generator capacity to power 100% of critical systems indefinitely.
Review the structure and training of emergency response teams, including 24/7 availability, decision-making authority, and regular drill frequency. Assess redundancy in cooling infrastructure, including N+1 or N+2 redundancy planning, preventive maintenance programs, and mean time to repair metrics for critical equipment.
Evaluate procedures for responding to temperature excursions, including product rescue capabilities, alternative storage arrangements, and transportation contingencies. Review notification procedures for emergencies, including escalation pathways, client communication templates, and service level agreements for different types of incidents.
7. Sustainability Practices and Energy Efficiency
Environmental performance increasingly impacts both cost structure and corporate sustainability goals. Compare energy usage per cubic foot of cold storage space against industry benchmarks, as well as trends showing improvement over time.
Assess the provider’s transition status to low-global warming potential refrigerants and leak detection/prevention programs, which impacts both environmental footprint and regulatory compliance. Evaluate the percentage of operations powered by renewable energy sources, including on-site generation and renewable energy credits.
Review water usage for cooling towers and other systems, including recycling programs and efficiency improvements and assess programs for reducing packaging waste, managing product obsolescence, and diverting operational waste from landfills.
Conclusion
As supply chains grow increasingly complex and consumer expectations for quality continue to rise, specialized cold storage 3PLs have become essential partners for businesses handling temperature-sensitive products. Beyond basic warehousing and transportation, networks like Cahoot offer expertise, technology, and purpose-built infrastructure that can support and ensure product integrity throughout the distribution lifecycle regardless of your specialized needs, be it cold storage, electronics, cosmetics, or anything else.
By leveraging the specialized capabilities of cold storage 3PLs, organizations can focus on their core competencies while gaining access to best-in-class cold chain management. The result is enhanced product quality, reduced waste, stronger compliance, and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction.
For businesses dealing with temperature-sensitive products, the right cold storage 3PL isn’t merely a service provider; they’re a strategic partner in delivering quality, compliance, and competitive advantage in an increasingly demanding marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Types of Products Need to be Stored in a Cold Storage Facility?
Fresh produce, meat, seafood, dairy products, frozen foods, pharmaceuticals commonly require specific temperature control.
How Do You Ensure Product Quality During Cold Storage?
Continuous temperature monitoring systems, regular quality checks, proper handling procedures, and adherence to industry standards maintains product quality during storage.
What Certifications are Needed to Ensure Cold Storage Food Safety and Quality?
Depending on the industry, certifications like BRCGS, FDA, or GMP may be required.

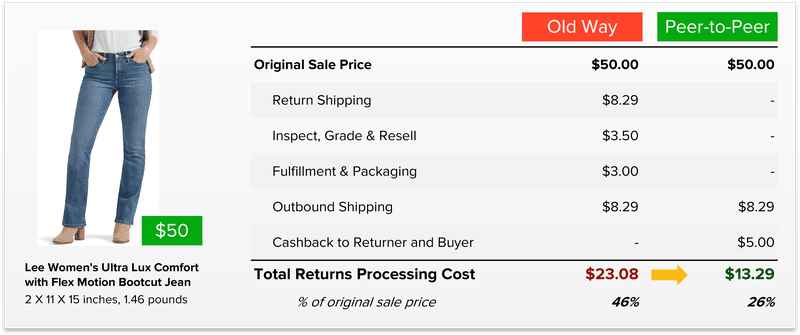
Up to 64% Lower Returns Processing Cost